Adverb Clause
1. What is an Adverb Clause?
An adverb clause (or adverbial clause) is a clause that works as an adverb in a sentence. Its role is to show place, time, condition, degree, and so on, by answering questions like “where?”; “when?”; “how?”; and “why?” Just like an adverb, it modifies other parts of a sentence to add more details.
Like all clauses, an adverb clause has a subject and a predicate. However, an adverb clause is a dependent clause—so, it can never be a sentence on its own. Specifically, an adverb clause is a modifier that modifies the independent clause.
2. Examples of Adverb Clause
As mentioned, adverb clauses answer questions like where, when, why and how. Here, the adverb clauses are underlined:
- Wherever they have carrots, you will find the rabbit. Where is the rabbit?
- After the rabbit arrived, he ate carrots. When did the he eat carrots?
- He ate carrots because he loves them. Why did he eat carrots?
- The rabbit ate carrots with his big square teeth. How did he eat carrots?
In each example, the underlined adverb clauses modify the independent clauses (in green) in the sentence. For instance, the adverb clause “wherever they have carrots” modifies the clause “you will find the rabbit.”
Notice the underlined adverb clauses are not complete sentences. An adverb clause is dependent, so it always needs to be connected with an independent clause to make a full sentence!
3. Parts of Adverb Clauses
Like all clauses, adverb clauses have a subject and a predicate. In addition, they almost always begin with a subordinating conjunction.
a. Subject
A subject is the person, place, idea, or thing that a sentence is about. It’s the noun that is “doing” something in a clause or sentence. Sometimes a subject is only one word, but sometimes it includes modifiers, or can be a noun phrase or gerund.
b. Predicate
A predicate holds the action—it tells what the subject does. Often the predicate is just a verb, but it can also be a verb phrase: a verb plus its objects or modifiers. Here are three examples of different types of predicates in clause:
- The rabbit hopped. Single verb “hopped” = predicate
- The rabbit hopped very high. Verb “hopped” + modifier “very high” = predicate
- The rabbit hopped into a hole. Phrase “hopped into a hole” = predicate
c. Dependent “Marker” Words/Subordinating Conjunctions
A dependent marker word (also called a subordinating conjunction) is a word that adds details like time or context. Most adverbial clauses start with a subordinating conjunction. Here’s a list of the most commonly used subordinating conjunctions:
d. Objects
Most adverb clauses also include objects. An object is the word affected by the verb or preposition in a sentence, usually nouns or pronouns that answer questions like “who,” “what,” “where,” and “when?” Look at these examples, with the objects underlined:
The rabbit ate carrots. What did the rabbit eat?
The rabbit hopped into a hole. Where did the rabbit hop into?
You can see that the underlined objects answers the questions. In the first example, “carrots” is affected by the verb ate, because they get eaten. In the second, “a hole” is affected by the preposition into.
4. Types of Adverb Clauses
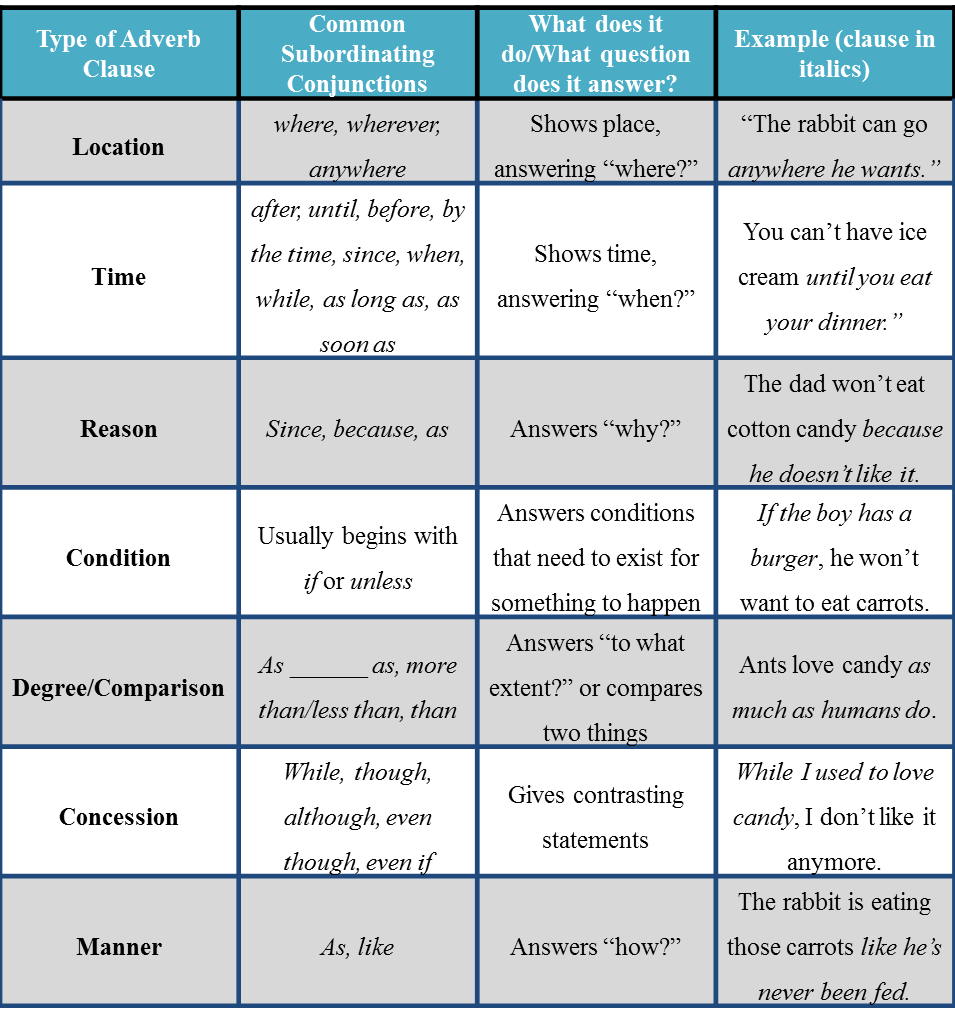
Adverbial clauses are very useful in sentences, and there are many types that express different things: location, time, reason, condition, degree/comparison, concession, and manner, among others. Here is a chart to help you understand the different types of adverb clauses.
5. How to Avoid Mistakes with Adverb Clauses
There are a few important things to remember about using adverb clauses:
- Adverb clauses are not complete sentences.
- They are dependent clauses, and must be paired with an independent clause.
- Adverb clauses begin with subordinate conjunctions.
- Subordinating conjunctions turn an independent clause into a dependent clause
- They help answer questions like “where”; “when?”; “why?”; and “how?”
- Adverb clauses, like all clauses, must contain a subject and a verb.
- Adverb clauses are different from phrases, which do not require a subject and a verb the way a clause does.
- Adverb clauses modify the independent clause in a sentence.
- They add more details, like time, location, reason, condition, degree, concession, and manner.
- An adverb clause should not affect a sentence’s grammar.
If you remove an adverb clause, the sentence should still be grammatically correct, like this:
The rabbit didn’t stop hopping until he got back to his hole. Complete sentence
Remove the adverb clause:
The rabbit didn’t stop hopping. until he back to his hole. Complete Sentence